Reading time: 5 minutes
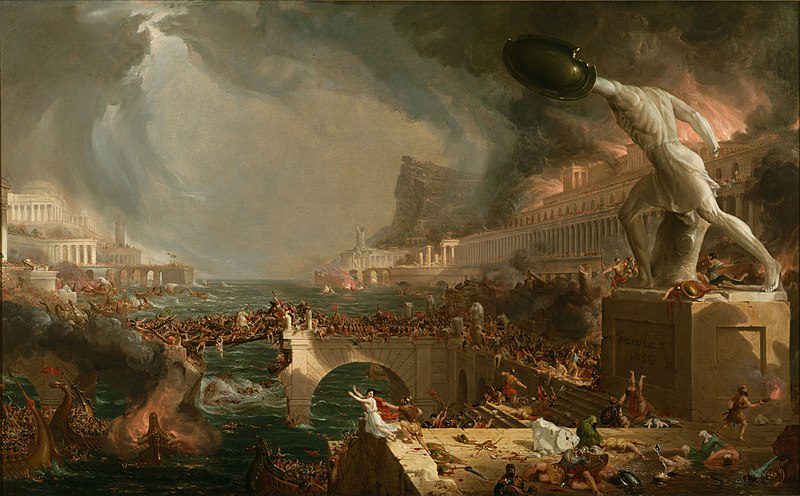
Leaving a major political body is nothing new for mainland Britain. In 409AD, more than 350 years after the Roman conquest of 43AD, the island slipped from the control of the Roman Empire. Much like the present Brexit, the process of this secession and its practical impacts on Britain’s population in the early years of the 5th century remain ill-defined.
As with the UK and Brussels, Britain had always been a mixed blessing for Rome. In around 415AD, St Jerome called the island “fertile in tyrants” (meaning usurpers) and late Roman writers portrayed a succession of rebellions in Britain, usually instigated by the army – many of whom would have been born in the province.
By Will Bowden, University of Nottingham
Around 407AD, the latest usurper, Constantine III, left Britain, taking the remaining elements of the army with him. The late Roman writer, Zosimus, then wrote that the pressure of Barbarian invaders obliged the British to throw off Roman rule and live “no longer subject to Roman laws but as they themselves pleased”, a phrase guaranteed to warm the heart of any Brexiteer.
This episode, around 409AD, seems to have been the end of Roman government in Britain. No “Romans” left, beyond the small number of soldiers who went to the continent to fight with Constantine III. Instead, the end of Roman Britain was, like the proposed present Brexit, a change in a relationship with a distant administration. But how did this change actually affect the people who lived in the island? And what were the consequences?
Roman life disappearing
One of the remarkable things about the first decades of the 5th century was the apparent speed with which the things we associate with Roman life disappeared.
The use of coins seems to have been an early casualty. Coins were always supplied by Rome to do the things that the Roman government cared about, such as pay the army. The latest coins to be sent to Britain in any number stopped in 402AD. Coin use may have continued in places for some years after, using older coins, but there was no real attempt to introduce local copies or substitutes (as sometimes happened elsewhere). This suggests there was no demand for small change or faith in the value of base metal coinage.

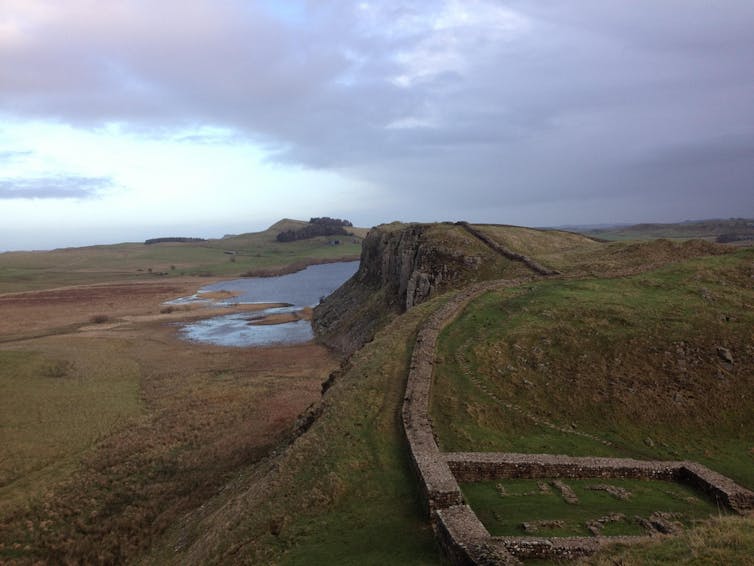
Industrial pottery manufacture (widespread in the fourth century) also vanished by about 420AD, while villas, some of which had achieved a peak of grandeur in the 4th century, were abandoned as luxury residences. Towns had already undergone dramatic changes, with monumental public buildings often abandoned from the 3rd century onwards, but signs of urban life vanish almost entirely after about 420AD. The forts of Hadrian’s Wall, beset by what the 6th-century writer Gildas termed “loathsome hordes of Scots and Picts”, seemingly turned from Roman garrisons into bases of local leaders and militias.
Many archaeologists have argued that the change was more drawn out and less dramatic than I’ve described. Equally, our own views of what is and isn’t “Roman” may not coincide with those held by people living during the 5th century. The notion of what was “Roman” was as complicated as “Britishness” is today. It’s also clear that many aspects of Mediterranean Roman life such as towns and monumental building never really took off in Britain to the extent that they did elsewhere in the empire and much of what we consider to be “Roman” never saw much enthusiasm across large parts of Britain. Nonetheless, we can be fairly certain that people quickly lost interest in things like coins, mosaics, villas, towns and tableware.

What came next
Although external forces such as Barbarian invasion are often blamed for the end of Roman Britain, part of the answer may lie in changes to the way that people living in Britain viewed themselves. During the 5th century once Britain was no longer part of the Roman Empire, new forms of dress, buildings, pottery and burial rapidly appeared, particularly in the east of Britain. This may be partly associated with the coming of the “Germanic” immigrants from across the North Sea whose impacts are so bemoaned by writers such as Gildas. However, the change was so widespread that the existing population must also have adopted such novelties as well.
Paradoxically, in western Britain, at places like Tintagel, people who had never shown much interest in Mediterranean life began in the 5th and 6th centuries to behave in ways that were more “Roman”. They used inscriptions on stone and imported wine, tablewares (and presumably perishable goods like silk) from the eastern Mediterranean. For these people, “being Roman” (perhaps associated with Christianity) assumed a new importance, as a way of expressing their difference from those in the east who they associated with “Germanic” incomers.
Archaeology suggests that late Roman Britain saw the same challenges to personal and group identities that the current Brexit debate stirs today. There can surely be little doubt that, had they lived in the 5th century, those who now identify as Leavers and Remainers would have debated the impact of foreign immigration and the merits of staying in the Roman Empire with equal passion. We must hope that some of the more dramatic changes of the 5th century, such as the disappearance of urban life and a monetary economy, do not find their 21st-century equivalents.
Originally published in The Conversation.
Podcasts about Britain after the fall of the Roman Empire:
Articles you may also like:

Weekly History Quiz No.246
1. Who created Knight, Death and Devil in 1513?
Try the full 10 question quiz.
The text of this article is republished from The Conversation in accordance with their republishing policy and is licenced under a Creative Commons — Attribution/No derivatives license.