The Beginning of Rebellion: The Hidden History of the 1521 Santo Domingo Slave Revolt
Reading time: 5 minutes
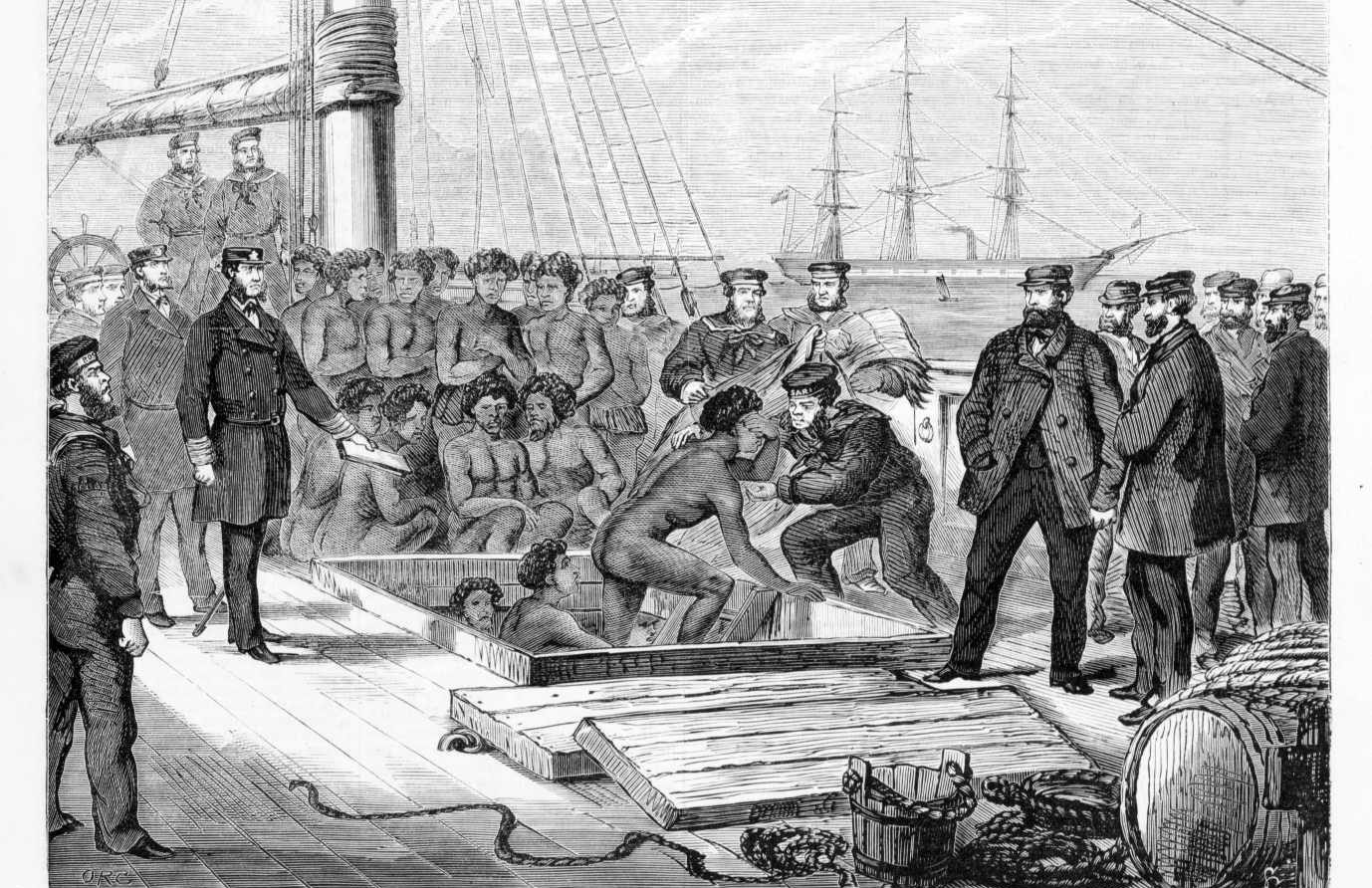
As the Age of Discovery slowly transitioned into the Age of Colonialism, the Spanish Empire, or more accurately its citizens, began importing African slaves into its new colonial holdings in North America and the Caribbean.
Only 30 years after Columbus had discovered the Americas, on the island of Hispaniola (now modern-day Haiti and the Dominican Republic), the very first colonial slave revolt occurred.