The History Guild Weekly History Quiz.
See how your history knowledge stacks up.
Have an idea for a question? Suggest it here and we’ll include it in a future quiz!
Want to know a bit more about the questions in the quiz, or the story behind them? Read on!
1. What year did the Mongol empire reach it’s greatest extent?
1294 – Originating from the Mongol heartland in the Steppe of central Asia, by the late 13th century it spanned from the Pacific Ocean in the east to the Danube River and the shores of the Persian Gulf in the west. At its peak, it covered some 9 million square miles (23 million square km) of territory, making it the largest contiguous land empire in world history.
2. Before Railways took over in the 1840’s what was the main way goods were transported around Britain?
Canal boats – Similarly to the Railway mania of the 1840’s there was a Canal mania, which was the period of intense canal building in England and Wales between the 1790s and 1810s.
3. The Battle of Rorke’s Drift was part of which conflict?
Anglo-Zulu War – The successful British defence of the mission station of Rorke’s Drift, began when a large contingent of Zulu warriors broke off from their main force during the final hour of the British defeat at the day-long Battle of Isandlwana on 22 January 1879, diverting 6 miles (9.7 km) to attack Rorke’s.
Just over 150 British and colonial troops defended the station against attacks by 3,000 to 4,000 Zulu warriors. The massive but piecemeal attacks by the Zulu on Rorke’s Drift came very close to defeating the much smaller garrison, but were consistently repelled. Eleven Victoria Crosses were awarded to the defenders.
4. Which of these leaders did NOT see combat in WW1?
Franklin Roosevelt – He was Assistant Secretary of the Navy during WW1 but never saw combat. Both Hitler and Mussolini were a Corporals. Churchill began the war as the First Lord of the Admiralty, a position he was removed from after the Gallipoli campaign. He then served as a battalion commander on the western front.
5. Why is the Domesday book such an important historical document?
It is the oldest public record in England and the most significant historical survey in the history of Europe – Domesday is a manuscript record of the “Great Survey” of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William the Conqueror. The survey’s main purpose was to determine what taxes had been owed during the reign of King Edward the Confessor, thereby allowing William to reassert the rights of the Crown and assess where power lay after a wholesale redistribution of land following the Norman conquest.
6. What was Joan of Arc’s role in the Hundred Year’s War?
She led the French to victory over the English resulting in the crowning of Charles VII of France – Read more about Joan of Arc here.
7. In 1817 Baron Karl von Drais invented the first bicycle. What was it’s nickname?
Dandy Horse – The dandy-horse was a two-wheeled vehicle, with both wheels in-line, propelled by the rider pushing along the ground with the feet as in regular walking or running. The front wheel and handlebar assembly was pivoted to allow steering.
8. What tank is this?
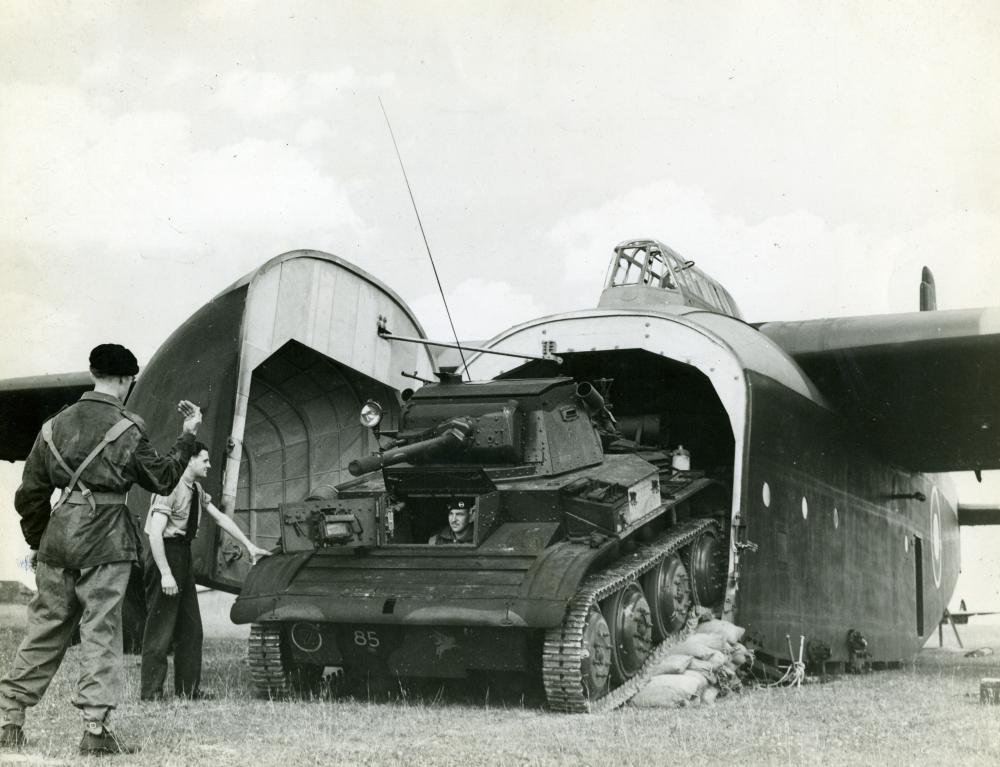

Tetrarch Light Tank Mk VII – Tetrarchs were attached to the 1st Airborne Division after it was decided that the design allowed its use as an air-portable light tank to support British airborne forces. The Tetrarchs were transported and landed in specially-designed General Aircraft Hamilcar gliders. The division used approximately twenty Tetrarchs during Operation Tonga, the British airborne landings in Normandy in June 1944. The tanks were landed by glider, where their appearance caused the Germans to cancel a counter-attack at a key moment in the battle but individually, they did not perform well. Several were lost in accidents and those that did see action proved to be inferior in firepower and armour to the armoured vehicles of the German forces.
9. Who was the first woman in space?
Valentina Tereshkova – Valentina Tereshkova was the first woman to go to space in June 1963 at the age of 26. The former textile worker had no experience as a pilot but was an avid skydiver. This experience proved to be of value as cosmonauts were required to parachute from their capsules upon returning to the Earth. After 18 months of training, Tereshkova launched into space on June 16, 1963 aboard her Vostok 6 spacecraft. During her three-day mission, she orbited the Earth 48 times. Following Tereshkova’s successful flight, the first program for women cosmonauts was scrapped. It would be nearly two decades before the next woman, cosmonaut Svetlana Savitskaya, would fly in space with her Soyuz T-7 mission in 1982.
10. What was the name of the communist guerrilla movement in Yugoslavia during WW2 that was commanded by Josip Broz Tito?
Partisans – The movement was consistently referred to as the “Partisans” throughout the war. According to a British observer ‘The partisan army had long since grown into a regular fighting formation comparable to the armies of other small States, and infinitely superior to most of them, and especially to the pre-war Jugoslav army, in tactical skill, fieldcraft, leadership, fighting spirit and fire-power.’
Articles you may also like

Cuba without Fidel: Five Years Later
Reading time: 6 minutes
For nearly 60 years, and for better or for worse, Fidel Castro was Cuba; at least he fancied himself as such, and the Communist Party which he largely governed with total control, never questioned this image. But what about the Cuban people? Did they really view Fidel as a “modern day Simon Bolivar”, and their one defender against American imperialism?

General History Quiz 151
1. Which was the first country to be ruled by a Fascist government?
Try the full 10 question quiz.