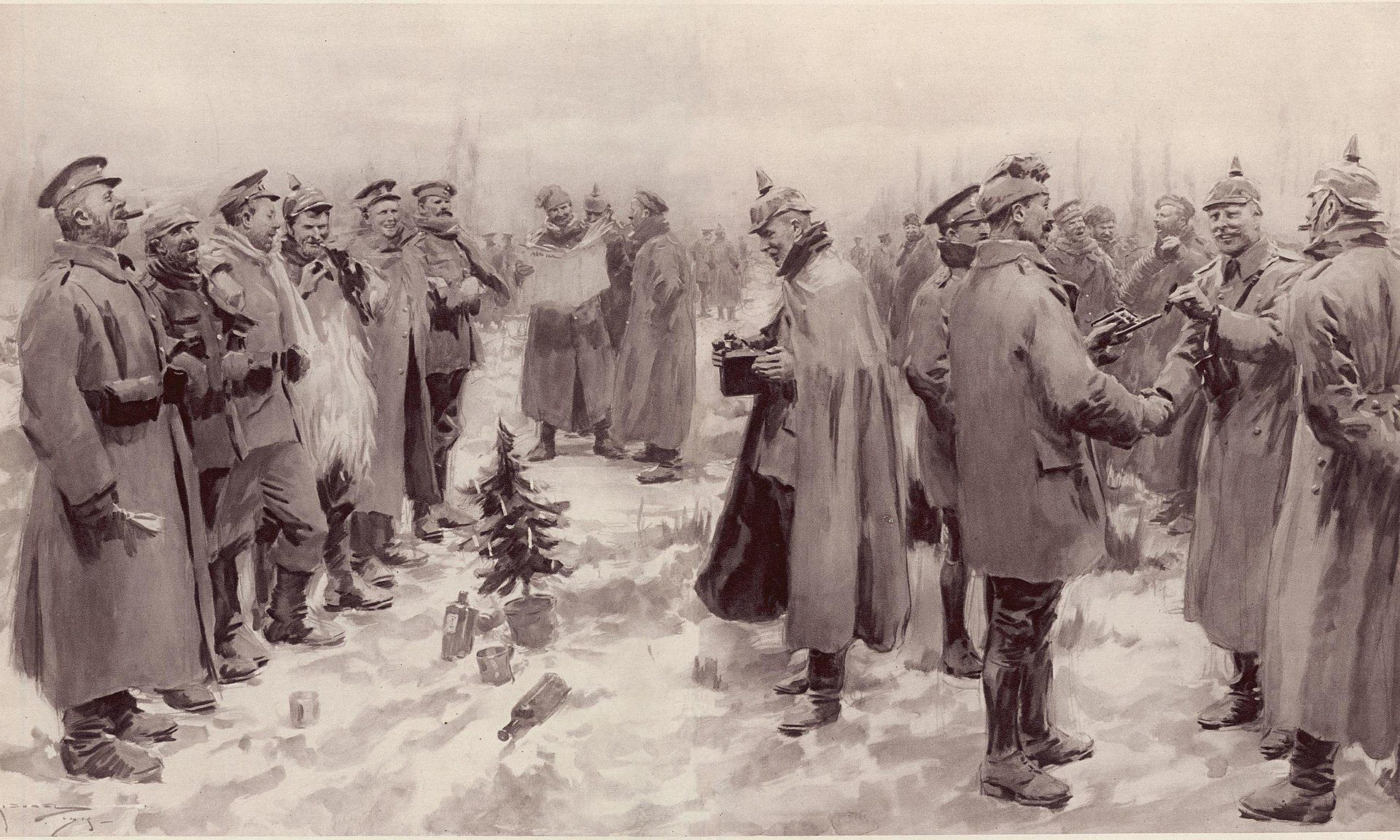
Flies, filth and bully beef: life at Gallipoli in 1915
Reading time: 6 minutes
Many factors contributed to making the Gallipoli battlefield an almost unendurable place for all soldiers. The constant noise, cramped unsanitary conditions, disease, stenches, daily death of comrades, terrible food, lack of rest and thirst all contributed to the most gruelling conditions.

The Strangest Battle of World War II? Uncovering the Battle of Castle Itter
Reading time: 6 minutes
In the waning hours of the war, exactly five days after Hitler shot himself in his bunker, a bizarre battle would commence in a small Austrian town, just south of the German border.
Seven hundred years after its construction in the 1200s, Castle Itter would host a battle between the Waffen-SS (the Nazi party’s specialist paramilitary) and a combined force of defecting German Wehrmacht troops, American soldiers, Austrian resistance fighters, and various French political prisoners.

Free of the Trench: How British & Imperial Forces Overcame the Deadlock of the Western Front
Reading time: 12 minutes
The First World War came to an end just over 100 years ago, a mere moment’s time in human history. But as close as we are to it, a century is more than enough to surround that conflict with myth and misconception.
The image of the war on the Western Front, as brought to us through decades of outdated scholarship and popular fiction, is simple: two vast armies, each equipped with the latest murderous fruits of the industrial age, found they couldn’t decisively defeat one another in the field and so settled into a long, bloody, dirty, and consumptive war in which thousands of lives were thrown away every day, often for minuscule gains which would bring neither side meaningfully closer to victory.
The real story is more complicated. By 1916, it was plain to see that tactics like those championed by Haig, designed to draw out the enemy for a momentous set-piece battle, weren’t working, and even those neck-deep in the fight didn’t need the benefit of hindsight to recognise that.
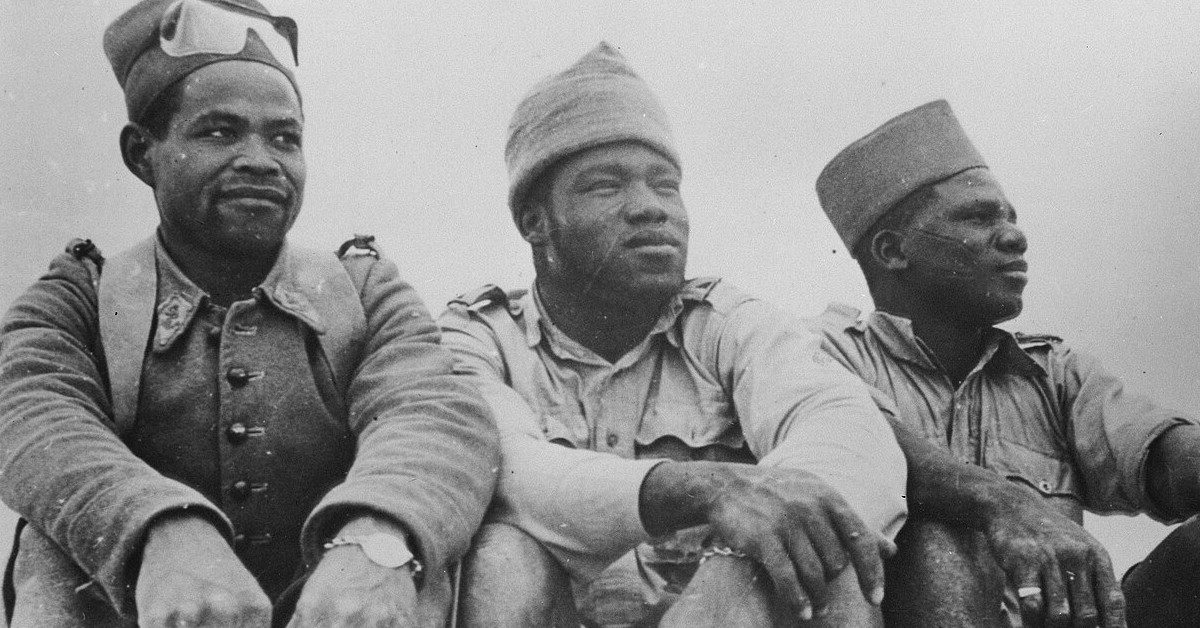

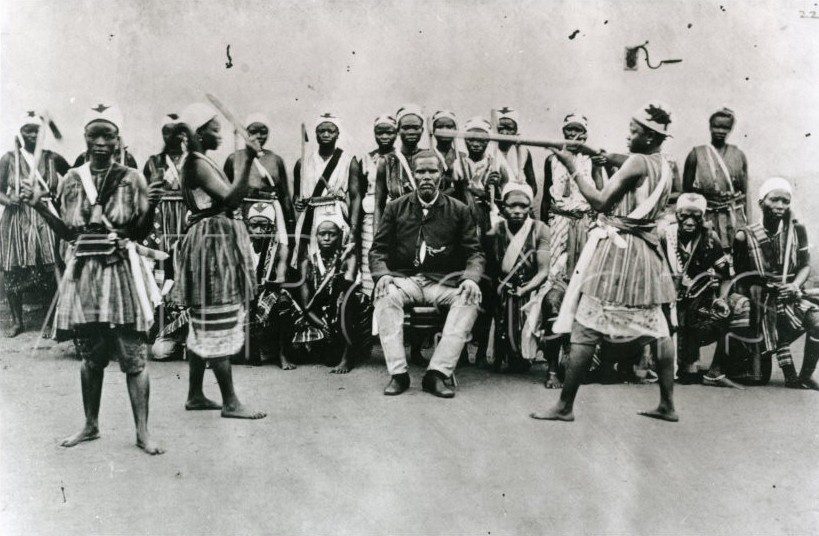
Free France was African: the Story of France’s African Soldiers in WW2
Reading time: 15 minutes
From a humble, precarious exile in London, Free France patched together from soldiers and sailors of the scattered French military under the leadership of General Charles de Gaulle. One of the most storied resistance movements in World War II, far-flung Frenchmen swelled in number until hundreds of thousands could return to liberate France in 1944.

The First World War continues: Medina, Arabia, January 1919
Reading time: 6 minutes
or many in the West, the First World War in the Middle East was a sideshow to the Western Front. The story of the wartime siege of Medina is even less well-known. But in the region it is still debated and contested, for example in December 2017 when the Foreign Minister of the United Arab Emirates accused Fakhri Pasha of stealing items from Medina, which earned a strong rebuke from the President of Turkey. The First World War in the Middle East had a profound effect on the region, with consequences to this day.

Why we don’t hear about the 10,000 French deaths at Gallipoli
Reading time: 6 minutes
With almost the same number of soldiers as the Anzacs – 79,000 – and similar death rates – close on 10,000 – French participation in the Gallipoli campaign could not occupy a more different place in national memory. What became a foundation myth in Australia as it also did in the Turkish Republic after 1923 was eventually forgotten in France.
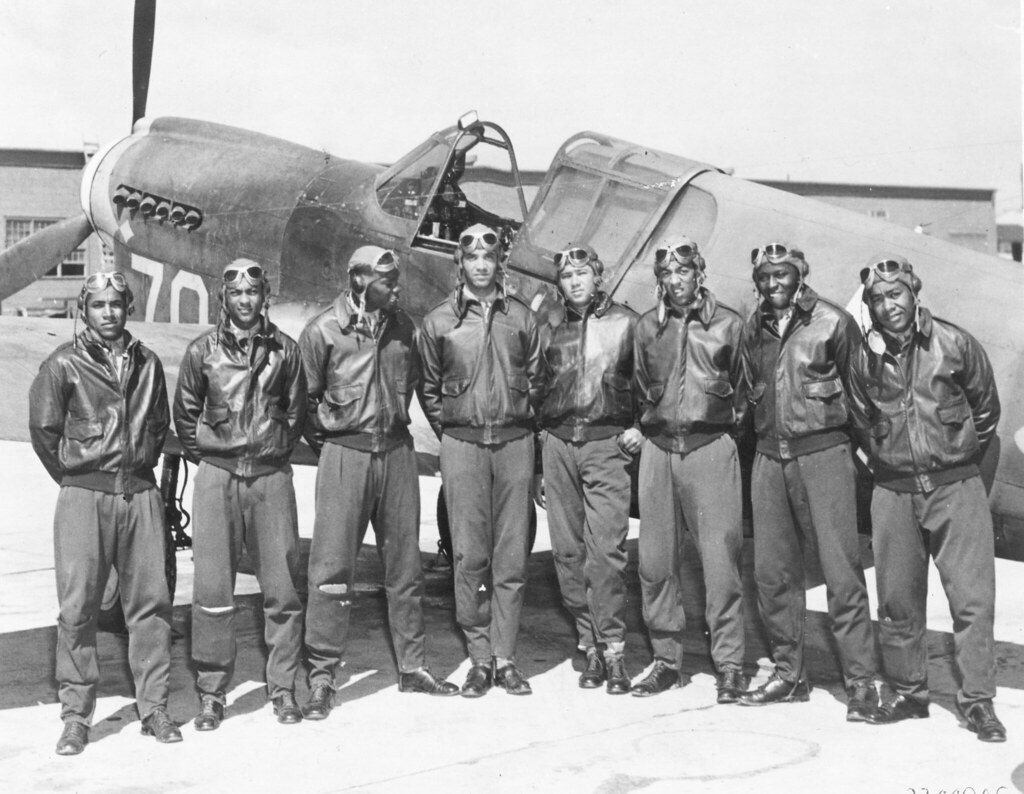

Where are All the Medals? Racial Bias in Military Bravery Awards
Reading time: 7 minutes
For service or for gallantry, almost all modern militaries – especially Western militaries, have issued war medals for a very long time.
But who decides who gets these medals and awards, and how?
Recent examination has brought to light a distinct lack of minority soldiers within Western militaries winning bravery awards, across many different countries, all throughout the 20th century and beyond.

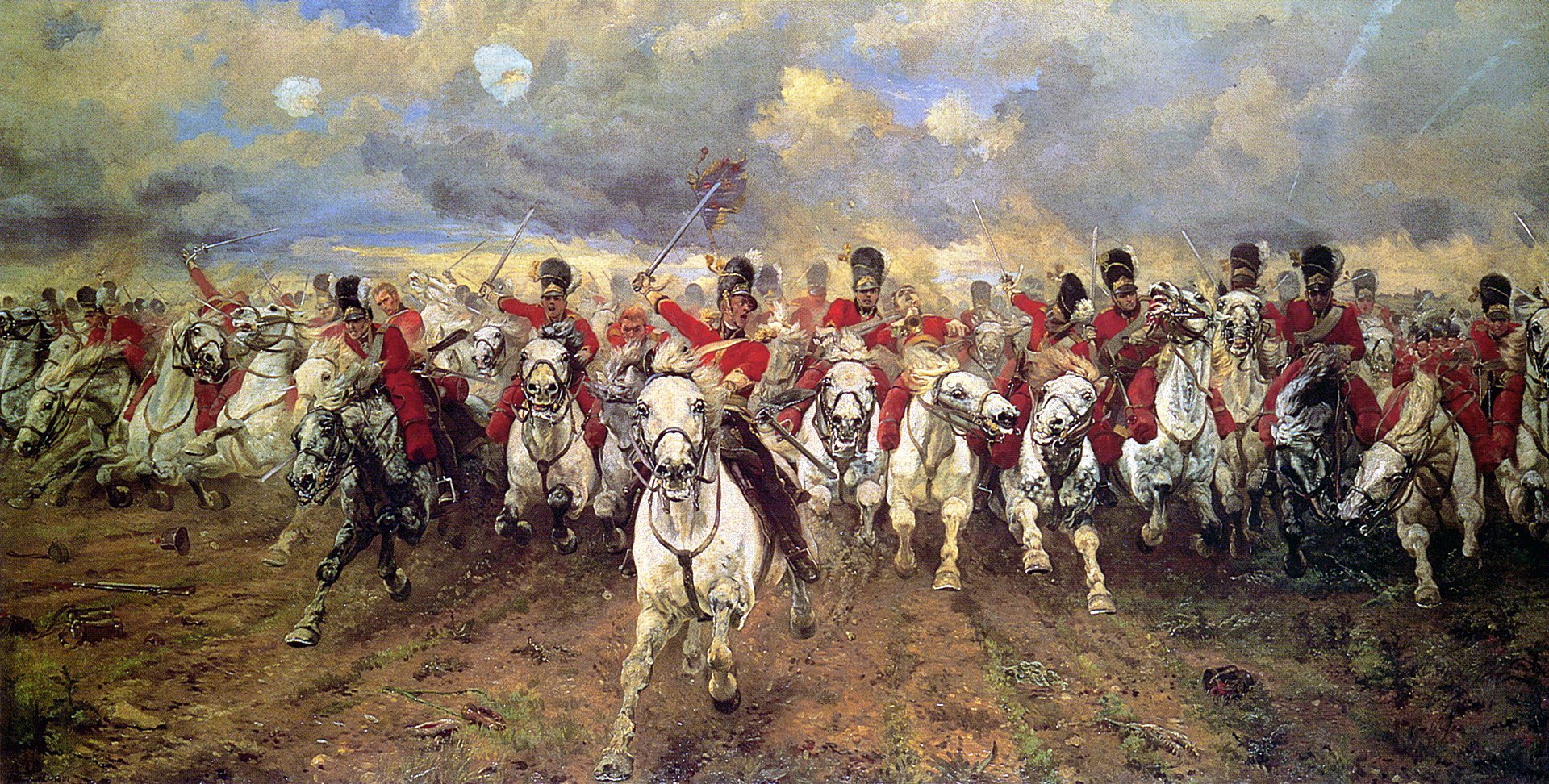
How the British defeated Napoleon with citrus fruit
Reading time: 5 minutes
Everyone knows that Britain’s conclusive victory over Napoleon was at Waterloo. The story of that day – the squares of infantry repulsing cavalry charges, the Imperial Guard retreating under murderous musket fire delivered by a red line of soliders, the just-in-time arrival of Field Marshal Blücher’s Prussian army – is one of excitement, horror and heroism. However, Britain’s biggest contribution to Napoleon’s defeat was much less romantic. It involved the first randomised controlled trial.
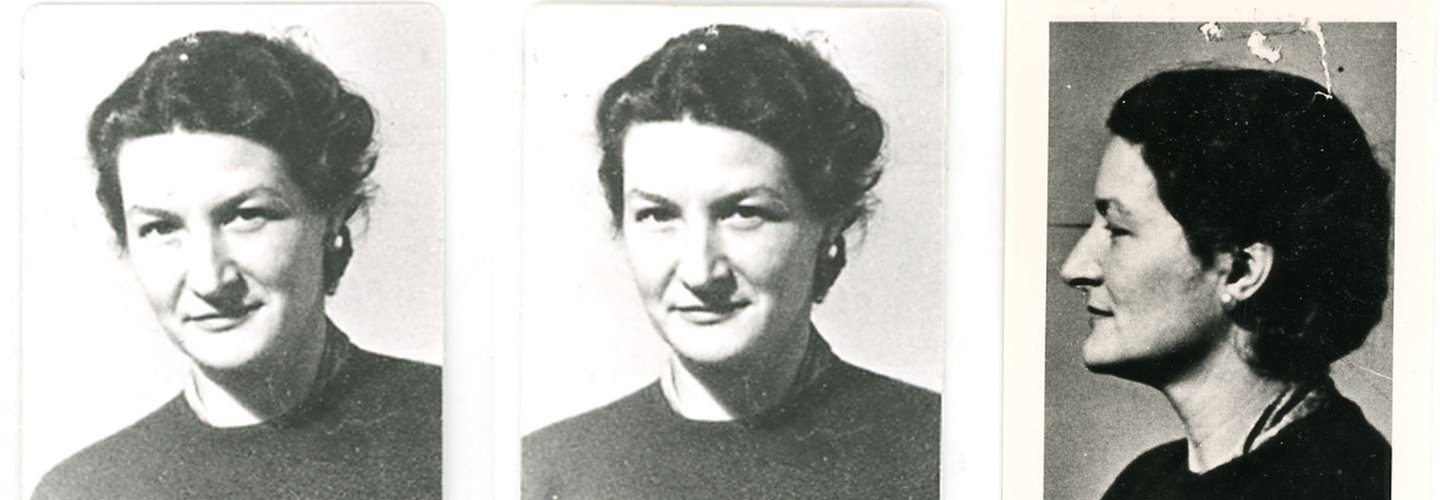

Virginia Hall, SOE Agent to CIA Pioneer
Reading time: 10 minutes
Virginia Hall (1906–1982) was an American woman who served with the British Special Operations Executive in France in 1941–1942. She then joined its US equivalent, the Office of Strategic Services, and became a founding member of the Central Intelligence Agency.

Australia’s long dread of France in the South Pacific
Reading time: 13 minutes
A striking duality drove Australia’s thinking about France in the 20th century. Expressed as a chant it went: In Europe, Good! In the Pacific, Bad!
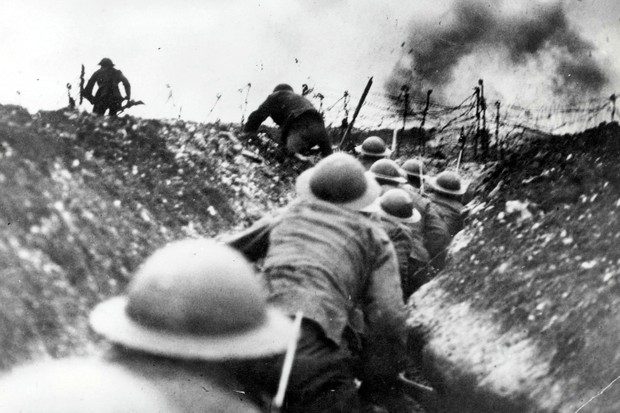

Ireland and the Battle of The Somme
Reading time: 8 minutes
The Somme was the first great action by a British Army on a continental scale. It was the longest, bloodiest battle of World War One, a campaign lasting four and a half months, and fought over a twenty-mile front near the Somme. In February 1916 Allied commanders had decided to launch an infantry offensive there,
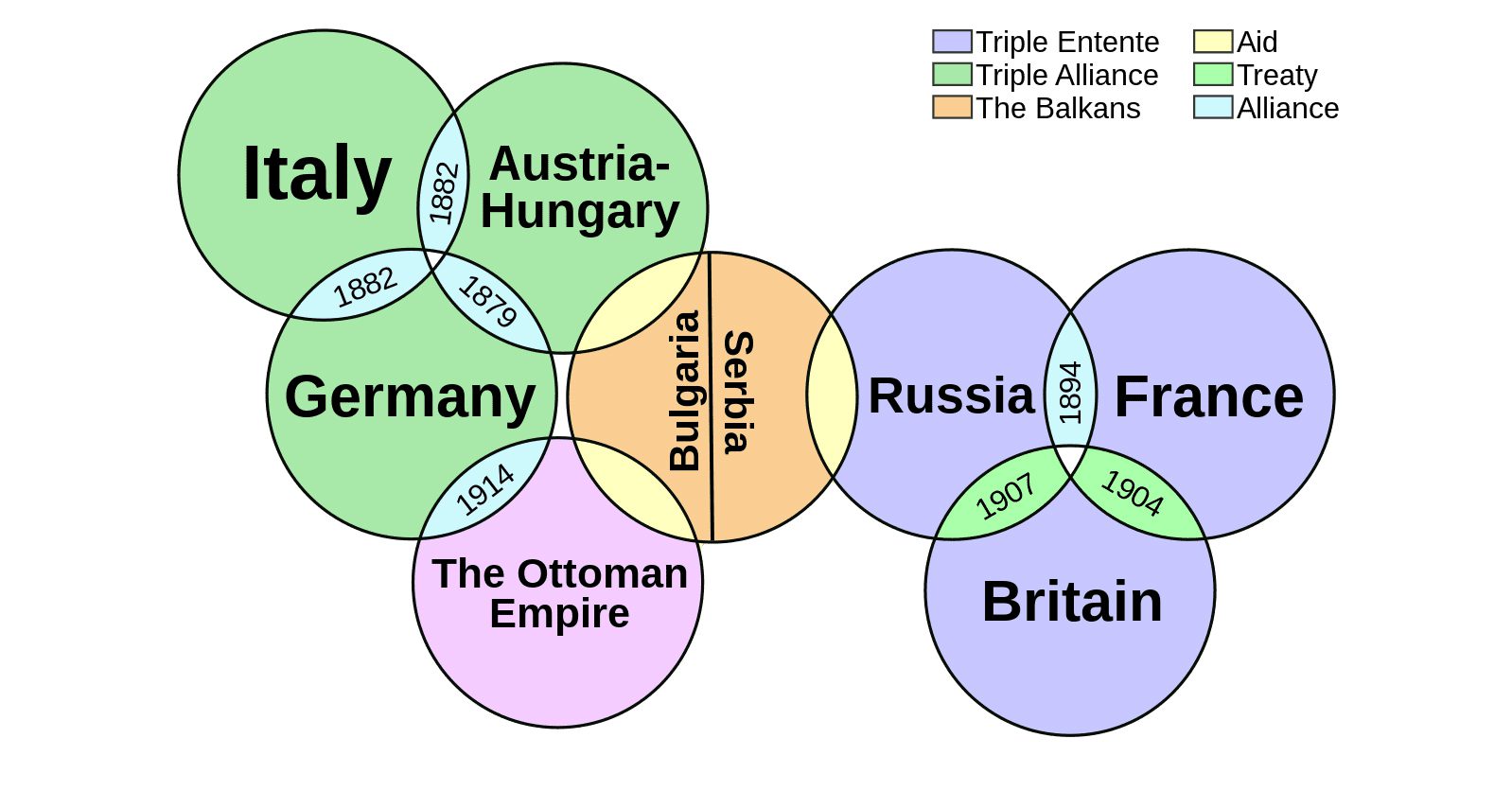
The debate on the origins of the First World War
Reading time: 5 minutes
The way historians have viewed the causes of WWI has changed in the hundred years since war broke out. This article explores the origins of the Great War.

The Saar Offensive 1939: When France invaded Germany
Reading time: 7 minutes
In September 1939, as German armies overran large swathes of Poland far to the east, the French launched an offensive of their own. Their goal was to capture the Saarland, the area between the French border and the German Siegfried line and force the Germans to transfer divisions away from Poland. The Saar Offensive of 1939 had begun.
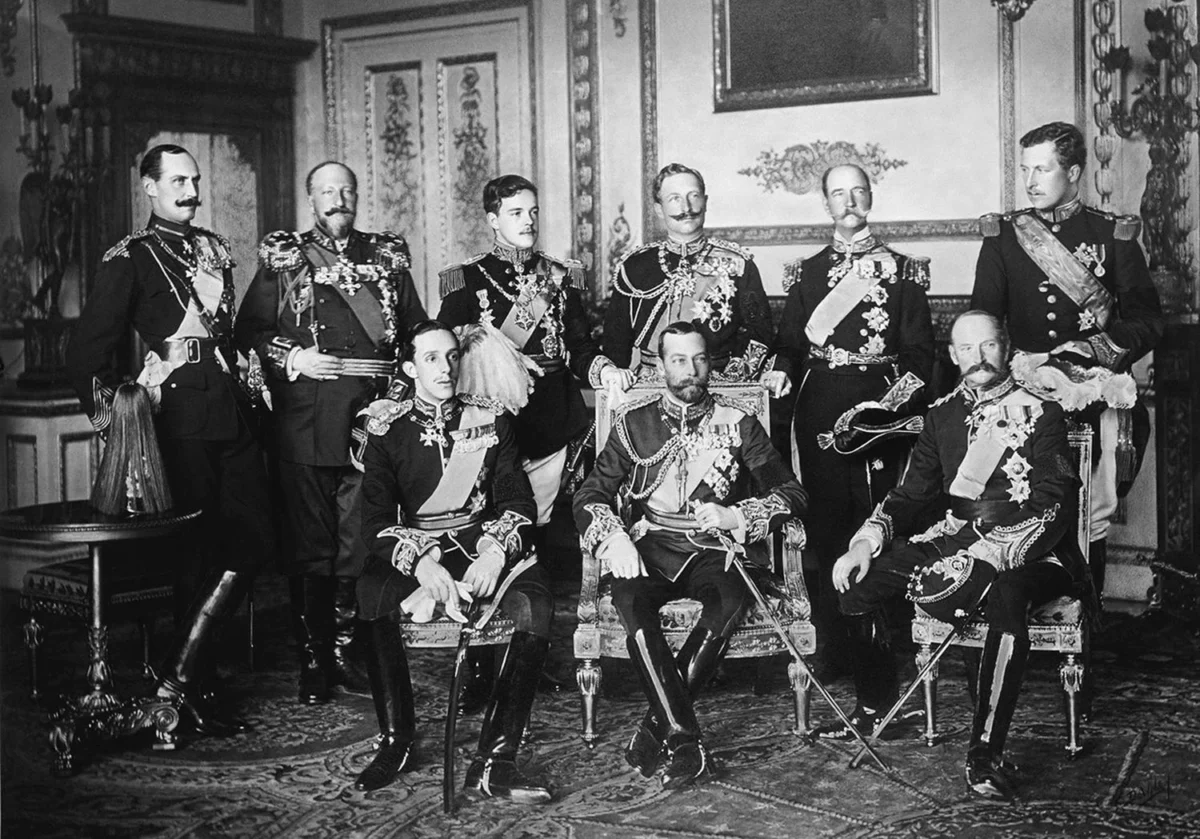

The debate on the origins of the First World War
Reading time: 5 minutes
The way historians have viewed the causes of WWI has changed in the hundred years since war broke out. This article explores the origins of the Great War.
How could the death of one man, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, who was assassinated on 28 June 1914, lead to the deaths of millions in a war of unprecedented scale and ferocity? This is the question at the heart of the debate on the origins of the First World War. Finding the answer to this question has exercised historians for 100 years.