November 12 @ 8:30 am – 4:30 pm at the East Malvern RSL, Melbourne
The Battle of the Beachheads was the bloodiest of all the Papuan campaigns. The resolve and tenacity of the Japanese defenders was, to Allied perceptions, unprecedented to the point of being “fanatical”, and had not previously been encountered. Please join a group of well-qualified speakers as we examine the Battle of the Beachheads in a one-day conference. This conference is organised by Military History and Heritage Victoria and supported by History Guild.
As the battle for Guadalcanal dragged on the Japanese advance on the Kokoda Track culminated and they were ordered to ‘advance to the rear’.
Two delaying defensive positions at Eora Creek and Oivi-Gorari imposed a toll on the Australians’ pursuit, but allowed time for the Japanese to complete a labyrinth of bunkers and trenches around the Papuan beach head villages of Gona, Buna and Sanananda.
The Battle for the Beachheads, as it became known, saw an estimated 9,000 Japanese troops in well-prepared positions defend to the death the territory they had occupied for the last six months. MacArthur ordered that the positions be destroyed and over the next two months Australian and US Army troops battled not only the resolute Japanese but swampy terrain, kunai grass, oppressive heat, heavy rain, sickness and disease to complete this difficult and brutal task.
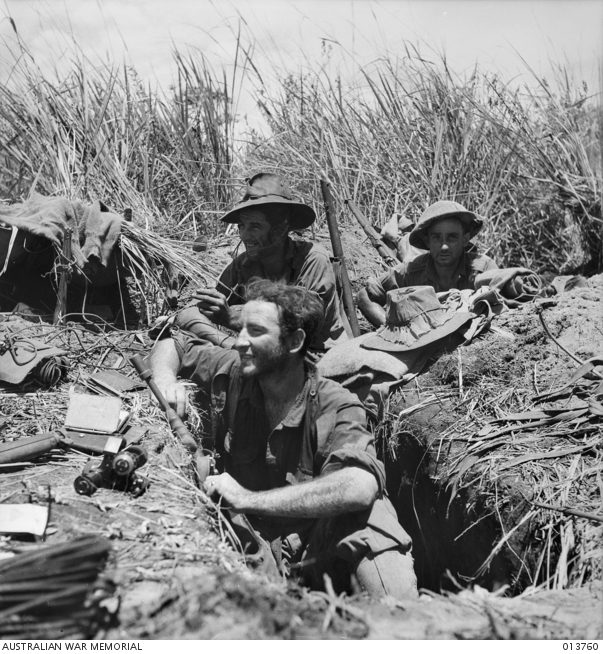

The Battle of the Beachheads was the bloodiest of all the Papuan campaigns. The resolve and tenacity of the Japanese defenders was, to Allied perceptions, unprecedented to the point of being “fanatical”, and had not previously been encountered. It was to mark the conduct of further battles throughout the remainder of the war. Securing victory at the Battle for the Beachheads cost Australia 1,261 dead and 2,210 wounded, and the Americans 734 dead and 2,037 wounded.
What was the Japanese plan? Who controlled the sea and the sky? How did the Allies mass forces onto the northern coast of Papua? Was the order to destroy the Japanese positions necessary? How well did the Australian and American forces cooperate in fighting the battle? Were Allied forces pushed beyond their capability? How much did tanks help to break the stalemate? What are the legacies of this little-known chapter of military history?
Please join a group of well-qualified speakers as we examine these and other questions in a one-day conference – The Bloody Beachheads: The Battles of Gona, Buna and Sanananda – on Saturday 12 November 2022 at the East Malvern RSL, Melbourne.
Find out More

The Battle of the Beachheads – Podcasts
By late 1942, the Allies had pushed the Japanese forces back along the Kokoda Track and were now down on the coastal plains of northern New Guinea. The Japanese may have been retreating, but they intended to hold the vital beachheads from Gona down through Sanananda to Buna. The fight to take the beachheads would be bloody and brutal, but first the Australians and their American comrades had to get there.

Japan’s Pacific War – Podcast
This podcast episode was commissioned by History Guild as part of our support of THE BLOODY BEACHHEADS: THE BATTLES OF GONA, BUNA AND SANANANDA – ONE DAY CONFERENCE. Angus Wallace, creator of the fantastic WW2 Podcast is joined by Peter Williams, author of Japan’s Pacific War: Personal Accounts of the Emperor’s Warriors.
Articles you may also like

Polygon Wood – Podcast
Following on from the success of the Battle of Menin Road, the 4th and 5th Australian Divisions took over from the 1st and 2nd Divisions to launch the attack at Polygon Wood. But the day before the battle is to commence, a strong German counter attack seized the ground which elements of the 15th Brigade were to attack from. It was a precarious situation which needed to be rectified immediately or else the whole attack could be thrown into confusion.
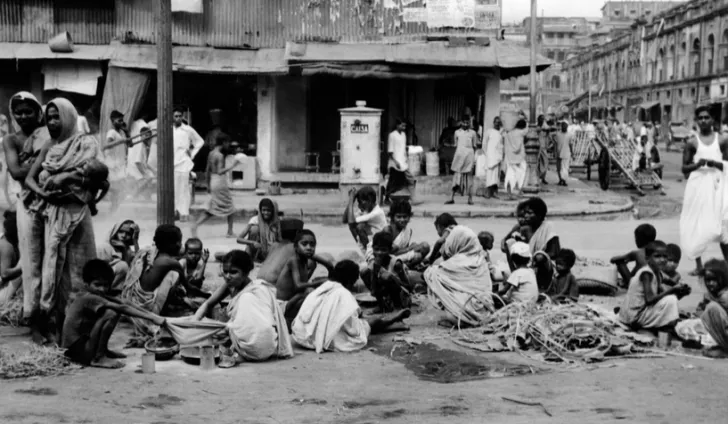

The legacy of Empire: The Bengal Famine
Reading time: 4 minutes
One of the motivations of The Things We Forgot To Remember is as an answer to the question “Why study history?” There are a lot of answers to this, but one important reason is that people are already talking about history, and sometimes, they have got it seriously wrong. One example of this is the widespread ignorance of the Bengal famine. For me, the ‘killer facts’ about the Bengal famine are straightforward. In 1941, when the Battle of the Atlantic was at its height, Winston Churchill and the War Cabinet considered the question of relative priority to give to imports of food, raw materials, and munitions.
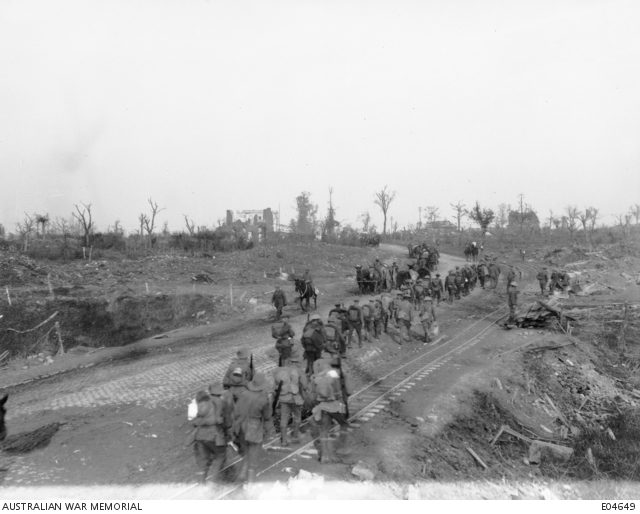

Menin Road – Podcast
In 1917, General Haig began what would become known as the Third Battle of Ypres, with the intention of capturing the village of Passchendaele. But getting to the village would require a series of bite-and-hold battles. In September, the 1st and 2nd Australian Divisions, along with British and South African Divisions, launched the third in the series of assaults, at Menin Road. For the first time in history, two Australian divisions would be fighting side-by-side. If they were to ever have this chance again, they would have to prove just how formidable they could be.
This article is published with the permission of the author. If you would like to reproduce it, please get in touch via this form.