History Guild General History Quiz 77
See how your history knowledge stacks up!
Want to know more about any of the questions? Once you’ve finished the quiz click here to learn more.
Have an idea for a question? Suggest it here and we’ll include it in a future quiz!
The stories behind the questions
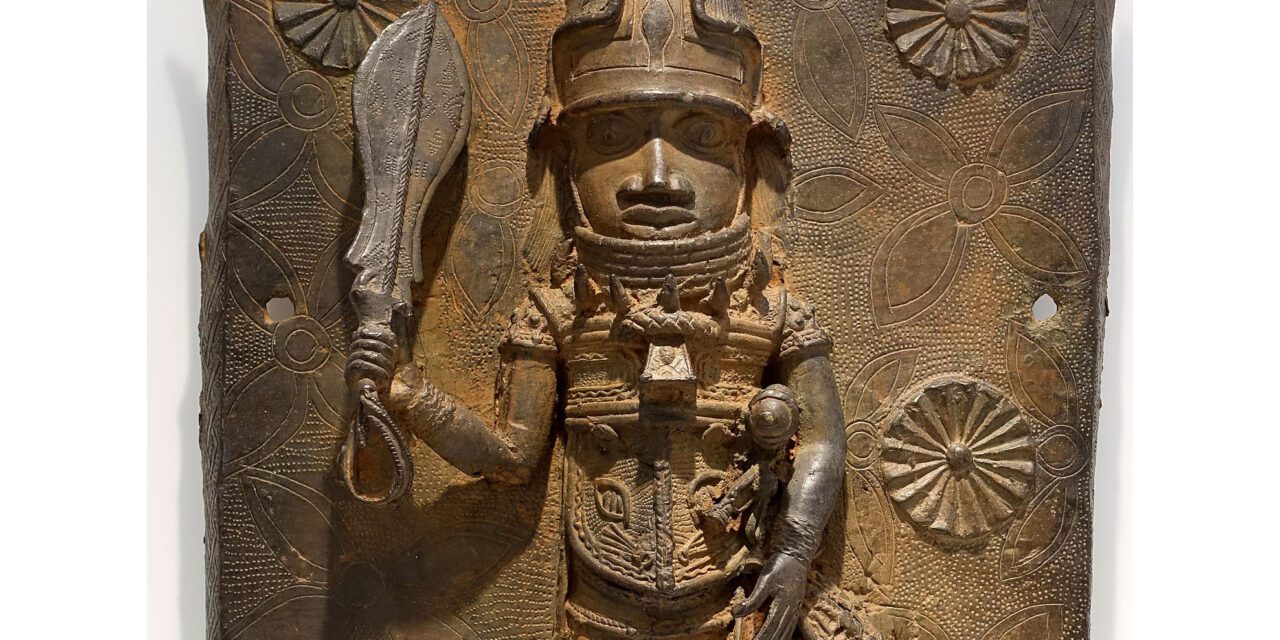
1. The Kingdom of Benin is now part of which country?
Nigeria – Kingdom of Benin is in what is now Nigeria. It is best known for the Benin Bronzes, a group of more than a thousand metal plaques and sculptures that decorated the royal palace. Most of the plaques and other objects were looted by British forces during the Benin Expedition of 1897 as imperial control was being consolidated in Southern Nigeria.
The Benin Bronzes are part of a contentious debate about the way in which they were acquired and whether they should be returned to Nigeria. Some have been returned, but only a small number. The British Museum holds over 200 pieces and has resisted calls to return them.
2. What was unique about the colony of Poyais?
It was invented in order to scam money from potential settlers – Gregor MacGregor managed to dupe many into believing that he had founded a nation in Latin America. Here, investors and settlers were told they would make a fortune from the established and extremely fertile lands of Poyais. How did this normal Scottish soldier convince hundreds of people to invest in his fake country in a scheme that, for many, would turn out to be deadly?
3. What year was Apartheid formally adopted by South Africa?
1950 – Apartheid was legally created by The Population Registration Act of 1950, which formalised racial classification and introduced an identity card for all persons over the age of 18, specifying their racial group. Official boards were established to determine peoples race, which lead to the separation of many families when members were allocated different races.
The Group Areas Act determined where one lived according to race. The Prohibition of Mixed Marriages Act prohibited marriage between persons of different races, and the Immorality Act made sexual relations with a person of a different race a criminal offence. Under the Reservation of Separate Amenities Act of 1953, municipal grounds could be reserved for a particular race, creating, among other things, separate beaches, buses, hospitals, schools and universities. Black South Africans were provided with services greatly inferior to those of whites, and, to a lesser extent, to those of Indian and Coloured people. Apartheid continued in South Africa until 1991.
4. Which American President gave the Gettysburg Address?
Abraham Lincoln – Beginning with the now famous phrase “Four score and seven years ago,” the Gettysburg Address is a speech that U.S. President Abraham Lincoln delivered during the American Civil War at the dedication of the Soldiers’ National Cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, on the afternoon of November 19, 1863, four and a half months after the Union armies defeated those of the Confederacy at the Battle of Gettysburg.
5. Where did Australian troops attack the French in 1941?
Syria – Operation Exporter was a little known, but very important campaign for the Australian military. It involved Australian’s fighting a strange war against confused Frenchmen who were not supposed to be our enemy. France had been defeated and subjugated by the Germans. The new French government, installed at Vichy, was answerable to the Führer. With France vanquished, the fate of their territories in Syria and Lebanon became uncertain.
Find out more about this fascinating Australian Campaign.
6. What caused the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion?
A faulty o-ring – The Space Shuttle Challenger disaster occurred on January 28, 1986, when the Space Shuttle Challenger broke apart 73 seconds into its flight, killing all seven crew members aboard. The explosion was caused by the failure of o-ring seals used in a joint that were not designed to handle the unusually cold conditions that existed at this launch. The seals’ failure caused a breach in the Solid Rocket Booster joint, allowing pressurized burning gas from within the solid rocket motor to reach the external fuel tank.
7. Which European country speaks a distinctive language that is derived from the ancient peoples of the Ural mountains?
Hungary – The Uralic languages form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25 million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Uralic-speakers arrived in the Baltic region from the East, specifically from Siberia, at the beginning of the Iron Age some 2,500 years ago.
8. Which Battle prevented the Japanese fleet from landing troops at Port Moresby in May 1942?
Battle of the Coral Sea – During the six months after the near simultaneous attacks on Pearl Harbour, the Philippines, Guam, Hong Kong and Malaya, the Allied forces desperately tried to stem the Japanese juggernaut. A string of Japanese victories left them masters of Southeast Asia with a foothold in the South West Pacific.
The US aircraft carriers Lexington and Yorktown and the Australian cruisers, Australia and Hobart, were in the Coral Sea. They were opposed by the Japanese invasion force, including three aircraft carriers. Both sides sustained heavy casualties, with the Japanese aircraft carrier Shōkaku and the USS Lexington both sunk. But the Japanese were forced to withdraw. With the option of a seaborne invasion denied them, the Japanese elected to take Port Moresby via a little known track called Kokoda. Read more about the battle.
9. This historic building is part of which modern city?

Istanbul – Hagia Sophia, officially the Holy Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque, and formerly the Church of Hagia Sophia, was the seat of the Patriarchate of Constantinople and a principal setting for Byzantine imperial ceremonies, such as coronations. Built in 537, it was the largest Christian church of the eastern Roman Empire (the Byzantine Empire) and the Eastern Orthodox Church. In 1453, after the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire, it was converted into a mosque. In 1935, the secular Turkish Republic established it as a museum. In 2020, it re-opened as a mosque.
10. When did Mao Zedong die?
1976 – following Mao Zedong’s death, Deng Xiaoping launched a program of reform that ultimately saw China become the world’s largest economy in terms of its purchasing power in 2014.