History Guild General History Quiz 190
See how your history knowledge stacks up!
Want to know more about any of the questions? Scroll down to learn more!
Have an idea for a question? Suggest it here and we’ll include it in a future quiz!
The stories behind the questions
1. Where did the Scythians originate?
Southern Siberia – A group of nomadic horse archers who began migrating westward around 900 BCE, they were wildly successful in defeating and subjugating many other peoples in Central Asia. Much of what we know about their culture comes from their well preserved burial mounds called Kurgens.
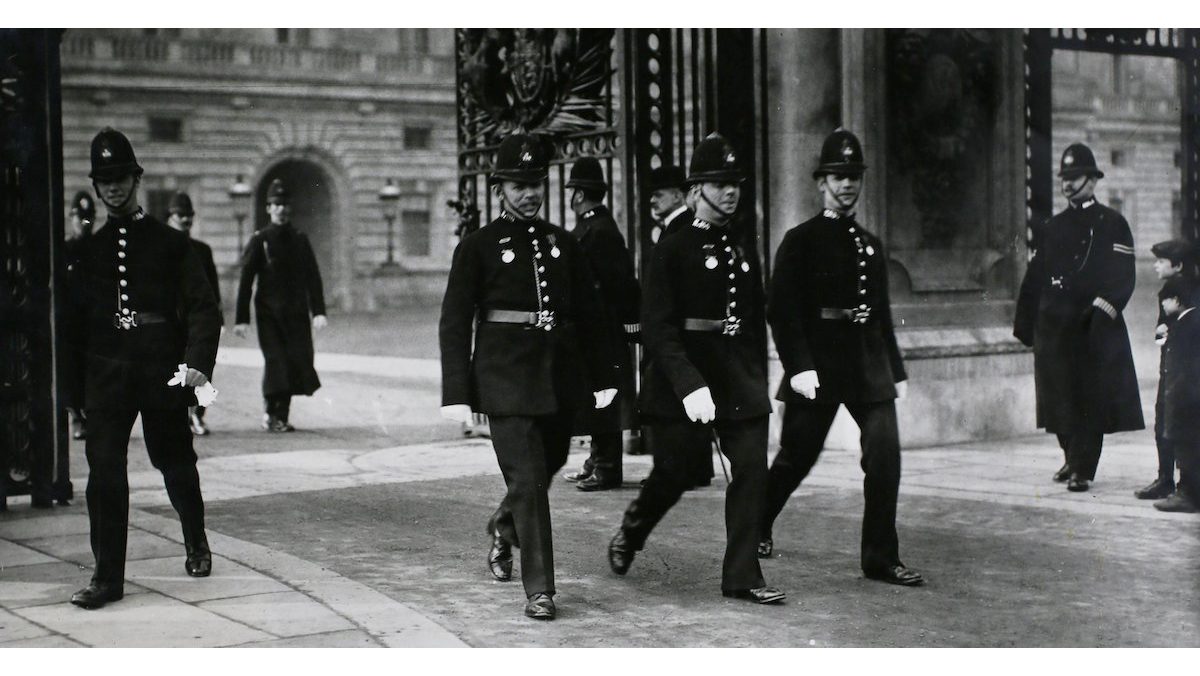
2. What action did Winston Churchill take when a Woman was first elected to the UK Parliament?
Refused to speak to her, saying that by ignoring her, he ‘hoped to freeze her out’ – In 1919, American born society hostess Nancy Astor won a Plymouth Sutton by-election for the Conservative Party, becoming the first woman MP to take her seat in the House of Commons. Astor was introduced into the chamber by her sponsors Arthur Balfour and David Lloyd George. She adopted plain clothing in the hope of avoiding scrutiny on her appearance and clothing choices, although the press continued to comment on it. In the lead up to Astor’s arrival, The Globe declared ‘When Lady Astor takes her seat in the House, the burning question for the moment is likely to be what she will do with her hat’.
She received a largely hostile reaction from male MPs, with Astor famously saying that members ‘would rather have had a rattlesnake than me’ in the House of Commons.
3. Which of these countries gained their independence first?
Zambia – 1964
Zimbabwe – 1980
Mozambique – 1975
New Caledonia – Remains a French Territory
4. Which country launched the first space station in 1971?
USSR – Salyut 1 was the world’s first space station, remaining in orbit for 6 months. The Salyut program followed this with five more successful launches of seven more stations.
5. When did Israel take the Gaza Strip from Egypt?
1967 – In reaction to the mobilization of Egyptian forces along the Israeli border in the Sinai Peninsula, Israel launched a series of preemptive airstrikes against Egyptian airfields, which destroyed nearly the entire Egyptian air force. The Six Day War followed, with Israel gaining control of the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt, the West Bank and East Jerusalem from Jordan, and the Golan Heights from Syria.
6. In 1956 which country saw a major uprising against its Soviet backed leaders?
Hungary – Hungarian Uprising of 1956 was a nationwide revolt against the government of the Hungarian People’s Republic and its Soviet-imposed policies, lasting from October 23 until November 10, 1956. Though initially leaderless, it was the first major threat to Soviet control since the USSR’s forces drove out Nazi Germany from its territory at the end of World War II and broke into Central and Eastern Europe.
More than 2,500 Hungarians and 700 Soviet troops were killed in the conflict, and 200,000 Hungarians fled as refugees. Mass arrests and denunciations continued for months thereafter. By January 1957, the new Soviet-installed government had suppressed all public opposition. These Soviet actions, while strengthening control over the Eastern Bloc, alienated many Western Marxists, leading to splits and/or considerable losses of membership for Communist Parties in the West.
7. What was the Iberian peninsula known as during its period of Muslim rule?
Al Andalus – Ruling substantial parts of modern Spain and Portugal from 711 and 1492, Al Andalus came to an end in with the fall of Granada in 1492.
8. Who was the most powerful ruler of the Carolingian Dynasty?
Charlemagne, Holy Roman Emperor – Charlemagne is known for his many reforms, including the economy, education, and government administration. From his capital, Aachen, he led his forces on a series of military campaigns, eventually ruling much of Western Europe.
9. Who was UN Secretary-General during the Six Day War?
U Thant – A skilled diplomat, Thant was born in Burma. He helped defuse the Cuban Missile Crisis and end the civil war in the Congo early in his term. He was criticised for his role leading up to the Six Day War, when Egypt expelled UN observers after Israel had refused to allow UN observers.
10. 160km north of Hadrian’s wall, which defensive structure extended Roman control into Scotland?
Antonine wall – 63km long, the wall crosses Scotland between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Construction began in 142 CE, 20 years after Hadrian’s wall was started. The Antonine wall was a less substantial barrier than Hadrian’s wall, and was abandoned only eight years after completion, with the garrison withdrawing to Hadrian’s wall.